- What is Ethical Hacking?
- List of Ethical Hacking Certifications
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certification
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
- Certified Penetration Testing Engineer (CPTE)
- Certified Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI)
- Certified in the Governance of Enterprise IT (CGEIT)
- GIAC Penetration Tester (GPEN)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional (CSSLP)
- How To Chose The Right Certification
- Jobs For Ethical Hackers
What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking is the practice of testing computer systems, networks, and applications to identify security vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can be exploited by malicious hackers.
Ethical hackers, use similar techniques and tools as malicious hackers to conduct their jobs, but the difference is that they do so with proper authorization obtained from the owners of those systems.
Ethical hacking is a crucial element in ensuring the security and safety of digital assets in today’s technology-driven world. It helps organizations proactively identify and fix security issues before malicious attackers can exploit them.
As the demand for skilled ethical hackers grows, certifications have become a way to demonstrate proficiency and stand apart from the crowds.
See Also
List of Ethical Hacking Certifications
In this article, I will discuss the top 11 certifications for ethical hacking to advance your career in the information and cybersecurity industry.
For each of these certifications, I will provide an overview and requirements for the certification.
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certification
The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification is one of the most popular and recognized certifications. CEH demonstrates an individual’s ability in identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in computer systems and networks, analyze risks and security threats, and provide proficiency in various countermeasures through lectures and hands-on labs.
It is often required by organizations for information security roles. CEH demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in ethical hacking, making them eligible for various job roles, such as, ethical hacker, penetration tester, and cybersecurity analyst. The certification also increases the individual’s earning potential and provides credibility to their skill set.
Requirements
The CEH certification covers various topics such as reconnaissance, enumeration, scanning networks, system hacking, web application hacking, and cryptography. The certification exam consists of 125 multiple-choice questions that test the individual’s knowledge and skills in these areas. The exam lasts for four hours.
EC-Council offers three different training options to prepare for the exam.

To earn the CEH certification, an individual must pass the 312-50v11 certification exam. The certification exam fee is $1,199, and individuals can take the exam at any Pearson VUE testing center globally.
Although there are no formal prerequisites for this certification, EC-Council recommends that candidates have at least two years of experience in the cybersecurity industry or they attend training through an accredited training center.
The training can be via the iClass platform, or an approved academic institution before taking the certification exam. The fee for this training is $850 if taken through the iClass platform.
CompTIA Security+
CompTIA Security+ is another popular certification that provides a strong foundation in cybersecurity principles and practices. The certification is recognized globally and is not tied to any specific technology or product. It also fulfills the DoD 8570 compliance
CompTIA+ provides a springboard to intermediate-level cybersecurity jobs. Security+ incorporates best practices in hands-on troubleshooting, ensuring candidates have practical security problem-solving skills required to:
- Assess the security posture of an enterprise environment and recommend and implement appropriate security solutions.
- Monitor and secure hybrid environments, including cloud, mobile, and IoT.
- Operate with an awareness of applicable laws and policies, including principles of governance, risk, and compliance.
- Identify, analyze, and respond to security events and incidents.
Overview
CompTIA Security+ certification covers a wide range of topics, including network security, cryptography, identity management, threat management, risk management, and vulnerability management.
The certification exam consists of 90 multiple-choice and performance-based questions. The exam length is 90 minutes, and the passing score is 750 on a scale of 100-900.
Benefits of the certification: CompTIA Security+ certification provides several benefits to professionals in the cybersecurity industry. It demonstrates that the individual has a foundational understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices, making them eligible for job roles such as security analyst, systems administrator, network administrator, and cybersecurity specialist. The certification also provides credibility to the individual’s skill set and increases their earning potential.
Requirements
To earn the CompTIA Security+ certification, an individual must pass the SY0-601 certification exam. The certification exam fee is $392 in the United States. Individuals can take the exam at any Pearson VUE testing center globally. There are no formal prerequisites for this certification but the following is recommended:
Recommended experience: CompTIA Network+ and two years of experience in IT administration with a security focus.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification is a globally recognized certification for information security professionals offered by (ISC)². It is considered to be one of the most advanced and prestigious certifications in the field of cybersecurity.
The CISSP is ideal for experienced security practitioners, managers, and executives interested in proving their knowledge across a wide array of security practices and principles, including those in the following positions:
- Chief Information Security Officer
- Chief Information Officer
- Director of Security
- IT Director/Manager
- Security Systems Engineer
- Security Analyst
- Security Manager
- Security Auditor
- Security Architect
- Security Consultant
- Network Architect
Overview
CISSP certification covers various topics such as security and risk management, asset security, security architecture and engineering, communication and network security, identity and access management, security assessment and testing, security operations, and software development security.
The certification exam consists of 250 multiple-choice questions that test the individual’s knowledge and skills in these areas. The exam lasts for six hours, and the passing score is 700 out of 1,000.
CISSP certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in various aspects of information security. The certification is recognized globally and is often required by organizations when hiring for cybersecurity roles.
Requirements
To earn the CISSP certification, an individual must have at least five years of full-time work experience in two or more of the eight domains covered in the certification exam.
CISSP Domains:
- Architect for Governance, Compliance and Risk Management
- Security Architecture Modeling
- Infrastructure Security Architecture
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Architecture
- Architect for Application Security
- Security Operations Architecture
Additionally, all individuals must pass the certification exam and adhere to the ISC2 Code of Ethics. There are also alternative paths to earning the CISSP certification, such as having four years of work experience and a relevant college degree.
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
OSCP certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in offensive security techniques, such as penetration testing and ethical hacking. The certification is offered by Offensive Security, a provider of cybersecurity training and certifications.
Overview
OSCP certification requires individuals to a 24-hour practical exam that tests their ability to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in computer systems and networks. The exam simulates a real-world penetration testing scenario, and individuals are required to exploit several vulnerabilities to achieve specific objectives.
Requirements
To earn the OSCP certification, individuals must pass a practical exam that requires them to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in a simulated environment.
There are no prerequisites for this certification but Offensive Security recommends knowledge in:
- Above-average understanding of TCP/IP networking.
- Beginner to advanced Linux and Windows administration experience.
- Familiarity with shell scripting: Bash or Python recommended.
To get their certifications they require that you take the PEN-200 (penetration testing with Kali linux) course. After that you take a 24 hour protored exam to get certified.
Certified Penetration Testing Engineer (CPTE)
CPTE certification is a vendor-neutral certification that demonstrates an individual’s expertise in the field of penetration testing. The certification is offered by the Mile2 Cybersecurity Institute, which provides training and certification for information security professionals.
Overview
CPTE certification goes beyond what you learn as an ethical hacker. It covers five key elements of penetration testing:
- Information gathering (reconnaissance)
- Scanning
- Enumeration
- Exploitation
- Reporting
The certification exam consists of 100 multiple-choice questions that test the individual’s knowledge and skills in these areas. The exam lasts for four hours, and the passing score is 70%.
They do not require you to take any of their courses. On their website, it states that “If you believe that you have the knowledge required to pass the certification exam you may purchase the Certification Exam.” This gives you access to the online exam, a free exam preparation guide, and access to unlimited practice exams. The price of this is $500.
The other two options are to do Self Study+Exam and a Live training option.
Self Study option is $1,750 but is usually available for around $995.
Live training options depending on the course are priced between $3,000 and $4,000.
Requirements
There are no course requirements and you can move directly to taking the certification exam. But in general, the recommendation is to have skills in the following:
- A minimum of 12 months of experience in networking technologies.
- Knowledge of TCP/IP networking.
- Knowledge of Microsoft packages.
- Network+, Microsoft, Security+.
- Basic Knowledge of Linux is essential.
Certified Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI)
CHFI is another certification offered by EC-Council. This is a vendor-neutral certification that demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in investigating cybercrimes and conducting digital forensics investigations.
The CHFI certification gives participants (Law enforcement personnel, system administrators, security officers, defense and military personnel, legal professionals, bankers, security professionals, and anyone who is concerned about the integrity of the network infrastructure.) the necessary skills to perform an effective digital forensics investigation.
Overview
CHFI certification covers various topics such as:
- Digital forensics investigation processes.
- Forensic examination of Windows, Mac, and Linux systems.
- Network forensics.
- Database forensics.
The certification exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions that test the individual’s knowledge and skills in these areas. The exam lasts for four hours, and the passing score is 70%.
CHFI certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in digital forensics investigation techniques, making them eligible for job roles such as digital forensics investigator, cybersecurity analyst, and incident response manager.
Requirements
To earn the CHFI certification, individuals must complete the CHFI training course offered by the EC-Council. The course includes various hands-on labs and exercises that simulate real-world digital forensics investigation scenarios. Additionally, individuals must pass the certification exam and adhere to the EC-Council Code of Ethics.
EC-Council offers three pricing options for the required training in cyber security courses, ranging from $2,199 to $3,499.
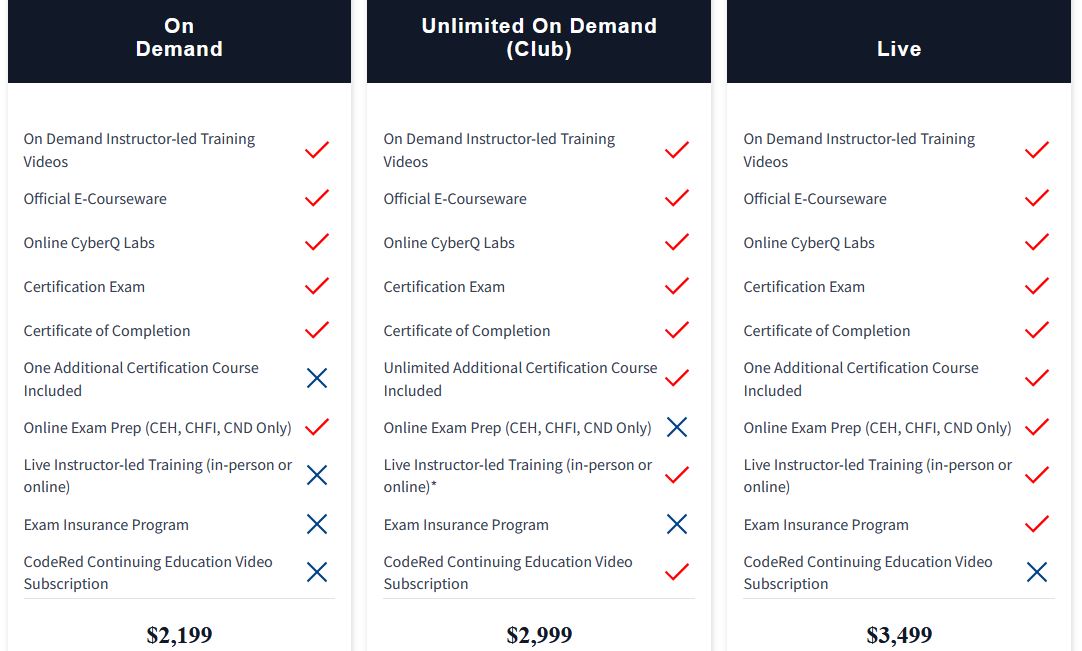
Certified in the Governance of Enterprise IT (CGEIT)
CGEIT certification is framework agnostic and the only IT governance certification for the individual. The certification is offered by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), a global nonprofit association.
Overview
CGEIT certification covers various topics such as IT governance frameworks, strategic alignment, risk management, value delivery, and performance measurement.
The certification exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions that test the individual’s knowledge and skills in these areas. The exam lasts for four hours, and the passing score is 450 out of 800.
CGEIT certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in IT governance, making them eligible for job roles such as IT governance manager, IT audit manager, and IT compliance manager.
The CGEIT manual for this certification is sold for $139 (non-member) pricing. They also have a CGEIT Q&A with explanations database priced at $399 (non-members).
The cost of the certification exam is $760 for non-members and $575 for members.
Requirements
To earn the CGEIT certification, individuals must have a minimum of five years of experience in IT governance, including at least one year of experience in a management role. They must also pass the CGEIT certification exam and adhere to the ISACA Code of Ethics.
GIAC Penetration Tester (GPEN)
The GIAC Penetration Tester, GPEN certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in conducting ethical hacking and penetration testing activities. The certification is offered by GIAC.
Overview
GPEN certification covers various topics such as reconnaissance, scanning, enumeration, exploitation, post-exploitation, and reporting. In this respect, it is similar to the OSCP certification.
The certification exam is proctored and consists of 82 questions and lasts for three hours. The passing score is 75%.
The cost of the GIAC GPEN certification is $949.
Being GPEN certified opens up opportunities for roles such as penetration tester, security analyst, and security consultant.
Requirements
To qualify for GPEN certification, individuals must have a minimum of two years of experience in information security and must complete the SANS SEC560: Network Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking course or demonstrate equivalent knowledge through industry experience.
Certification applicants must also pass the certification GIAC exam and adhere to the GIAC Code of Ethics.
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
CISM certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in managing, designing, and assessing enterprise-level information security programs. The certification is also offered by ISACA.
Overview
CISM certification covers topics such as information security governance, risk management, incident management, program development, and management. You will learn how to assess risks, implement effective governance and proactively respond to incidents.
Based on ANAB stats, 70% of the people experienced on-the-job improvement while 42% received a pay boost.
The certification exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions and is scheduled for four hours.
The cost of the certification exam is $760.
The CISM certification will help with closing knowledge and skill gap when applying for job roles such as information security manager, IT director, and chief information security officer.
Requirements
As a candidate for certification, you must have a minimum of five years of experience in information security, with at least three years in information security management.
Candidates must also adhere to the ISACA Code of Ethics and pass the CISM certification exam.
Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional (CSSLP)
CSSLP certification demonstrates an individual’s proficiency in designing, developing, and maintaining secure software applications. This certification is offered by (ISC)².
Overview
CSSLP certification covers topics such as:
- Secure software concepts.
- Requirement analysis
- Software design and implementation
- Software testing
- Maitenance
The certification exam consists of 125 multiple-choice questions.
The cost of the certification exam is $699.
CSSLP certification is ideal for software development, testers, and security professionals. People with the following job roles may benefit from this certification.
- Software Architect
- Software Engineer
- Software Developer
- Application Security Specialist
- Software Program Manager
- Quality Assurance Tester
- Penetration Tester
- Software Procurement Analyst
- Project Manager
- Security Manager
- IT Director/Manager
Requirements
A candidate is required to have:
- Minimum of four years of cumulative paid software development experience.
- Or three years of cumulative paid SDLC professional work experience in one or more of the eight domains of the CSSLP CBK with a four-year degree.
Candidates for the certification exam must also adhere to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics and pass the CSSLP certification exam.
How To Chose The Right Certification
With the increasing demand for cybersecurity professionals, obtaining a certification will be an excellent investment for your career.
However, with so many certifications it can be challenging to choose the right one. I would suggest that if you are already working, then ask around and find out what certifications others have in the positions you are aiming for. If you are searching for a new position then look at the job description for the roles you are targeting. The job descriptions will most likely list the certifications or education requirements.
Another way is to contact headhunters in firms specializing in placing people in new positions. They will usually have most up-to-date information on the certifications that are most in demand.
Listed below are some additional factors you may consider:
- Career Goals: Consider your career goals and choose a certification that aligns with your career aspirations.
- Cost: Certifications can be expensive, so consider your budget when selecting a certification. Some certifications require you to attend training courses, which can add to the overall cost. Although money is a major concern for most, I usually like to think of this as an investment and am willing to spend money to learn.
- Skill Level: Different certifications cater to different skill levels, ranging from beginner to expert. If you’re a beginner, you might want to consider starting with entry-level certifications such as CompTIA Security+ or CEH. If you have advanced skills, you can aim for OSCP or GPEN certifications.
- Reputation: Look for certifications that have a good reputation in the industry. Enough said. 🙂
- Maintenance Requirements: Some certifications require you to renew the certification periodically by obtaining continuing education credits or retaking the exam. This can be concern for some but the way I look at it is that you don’t need to renewthe certification unless there are significant updates in technologies and processes.
Jobs For Ethical Hackers
There are many different jobs and roles available for ethical hackers. Below is a somewhat exhaustive list of titles. In the future I will be publishing a post on title and salary with more detail. For now, just review the list and see what roles are of most interest to you.
- Application Security Analyst
- Chief Information Security Officer
- CND Cyber Analyst
- CND Fusion Analyst
- CND Security Specialist
- Computer Network Defense Intrusion Analyst
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Cyber Red Team Operator
- Cyber Network Defense (CND) Analyst
- Cyber Security Forensic Analyst
- Cyber Security Forensic Analyst
- Cyber Security Engineer
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Cyber Security Vulnerability Analyst
- Cyber Security System Engineer
- Cyber Security Engineer II
- Cyber Security Incident Response, Incident Analyst
- Cyber security Network Analyst
- Cyber Security Incident Response Engineer
- Cyber Threat Analyst
- Cyberspace Network Defense (CND) Technician
- Digital Forensic Analyst
- Global Security Assurance Analyst
- IT Security Compliance Specialist
- Information Security Analyst
- Information Security Associate – Insider Threat Analyst
- Information Security Engineer
- Information Security Manager
- IT Security Administrator
- Information System Security Officer
- L2 Security Analyst
- Network Analyst
- Network Security Engineer
- Penetration Tester
- Risk and Remediation Manager
- Risk Assessment- Security Consultant
- Security Consultant
- Security Analyst Tier 3
- Security Operations Analyst
- Security Incident Response Analyst
- Sr. Security Threat Analyst
- Systems Administrator
- Security Engineer
- Security Information Assurance Analyst
- Security Architect, Manager
- Software Security Analyst
- SOC Security Analyst
- Senior Cyber Security Monitoring Analyst
- Senior Information Assurance/ Security Specialist
- Technical Operations Network Engineer
- Tier 3 NSOC Analyst
- Technical Security Analyst
- Vulnerability Analyst
Check out our post on what ethical hacking is and how to become a hacker.