In the dynamic world of IT, efficieny and precision concerns are paramount. Windows Command Line prompts mostly overlooked by newbies are a potent tool for expert admins.
See Also
In the realm of Windows operating systems, administrators and tech enthusiasts often find themselves relying on the graphical user interface (GUI) for system management. This path may be easy to follow but does not offer flexibility that is available by using command line commands.
The biggest benefit of using command line utilities is the ability to include those command in shell scripts for automation.
In this post, I will explore essential command line prompts that can significantly enhance your capabilities and increase your productivity in Windows Administration and Monitoring.
What is CMD?
“CMD” typically refers to the Command Prompt on Windows operating systems. The Command Prompt is a text-based interface where users can interact with the operating system by typing commands. It’s sometimes also referred to as the “Command Shell” or “cmd.exe.”
The Command Prompt allows users to perform various tasks, such as navigating through the file system, running programs, and executing administrative commands.
Users can access the Command Prompt by searching for “cmd” or “Command Prompt” in the Start menu on Windows. The Command Prompt is a powerful tool for running batch scripts and automating repetitive tasks on Windows.
Shown below is output from running commands cd and dir.
D:\>cd temp
D:\temp>dir
Volume in drive D is D
Volume Serial Number is 6E09-C1EB
Directory of D:\temp
10/25/2023 04:35 PM <DIR> .
09/11/2023 02:30 PM <DIR> davinci
03/05/2023 05:13 PM 4,476 docker-compose.yml
01/08/2024 04:06 PM <DIR> downloads
12/02/2022 01:00 PM <DIR> important-to-update
10/19/2022 10:44 AM <DIR> nginxcache
09/13/2022 01:14 PM 1,798,493,311 projects.zip
04/14/2023 06:29 AM <DIR> windows
2 File(s) 7,735,325,744 bytes
5 Dir(s) 1,796,019,675,136 bytes freeWindows CMD: Command Line Prompt Examples
Navigating the File System
Before we get into other advanced commands, let’s review some of the basics CMD line prompts.
cd : Change Directory
Use the cd command to display the name of a directory or change the current directory.
Syntax: CD [/D] [drive:][path]
Example: Shown below I am in the root C drive folder \. To change to the temp folder I will use the cd command.
C:\>cd temp
C:\temp>dir : List Directory
Use the dir command to display the name of a directory or change the current directory.
Syntax: DIR [drive:][path][filename] [/A[[:]attributes]] [/B] [/C] [/D] [/L] [/N][/O[[:]sortorder]] [/P] [/Q] [/R] [/S] [/T[[:]timefield]] [/W] [/X] [/4]
As you can see this is a complex command and has many available options. I will only go over the very basics to show you how you can start with the command.
Example 1: In the example below type dir and press enter to see contents of a directory or folder.
E:\temp>dir
Directory of E:\temp
11/28/2023 05:59 AM <DIR> .
11/28/2023 05:59 AM <DIR> ..
03/09/2021 11:04 AM 15,138 apacheconfig.zip
10/25/2023 03:28 AM <DIR> completed
10/25/2023 06:29 AM <DIR> downloads
03/09/2021 11:04 AM 15,138 nginzconfig.zip
10/25/2023 04:13 AM <DIR> temp
12/01/2023 06:16 AM <DIR> torrent
mkdir : Make Directory
Use the mkdir command to create a new directory.
Syntax: MKDIR [drive:]path
Example: In the example below I created a subdirectory with the name abc using the dir command.
C:\temp>dir
Directory of C:\temp
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> abc
del : Delete files
Use the del command to delete one or more files.
Syntax: DEL [/P] [/F] [/S] [/Q] [/A[[:]attributes]] names
You can delete multiple files by separating the names with a space.
Example 1: In the example below I delete a file in a directory and then run the dir command to show that it is actually deleted.
C:\temp>dir
Directory of C:\temp
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> abc
01/09/2024 02:41 AM 4 file.txt
C:\temp>del file.txt
C:\temp>dir
Directory of C:\temp
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> abc
fc : Move files and rename files and directories
Compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them.
Syntax:
- Text file compare:
FC [/A] [/C] [/L] [/LBn] [/N] [/OFF[LINE]] [/T] [/U] [/W] [/nnnn] [drive1:][path1]filename1 [drive2:][path2]filename2 - Binary file compare:
FC /B [drive1:][path1]filename1 [drive2:][path2]filename2
Example:
move : Move files and rename files and directories
Compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them.
Syntax:
- Move one ore more files:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]filename1[,…] destination - Rename a directory:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
Example 1: In the first example I will use the move command to move newfile to file1.
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 newfile.txt
C:\temp>move newfile.txt file1.txt
1 file(s) moved.
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 03:08 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 03:08 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 file1.txtExample 1: In the example below I will use the move command to rename a directory.
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 03:11 AM <DIR> abc
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 file1.txt
C:\temp>move abc xyz
1 dir(s) moved.
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 file1.txt
01/09/2024 03:11 AM <DIR> xyzrmdir : Remove Directory
Remove or delete a directory.
Syntax: RMDIR [/S] [/Q] [drive:]path
Example: I will delete the folder I created in an earlier example.
C:\temp>dir
Directory of C:\temp
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:41 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:36 AM <DIR> abc
C:\temp>rmdir abc
C:\temp>dir
Directory of C:\temp
01/09/2024 02:44 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:44 AM <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 351,775,477,760 bytes freeren : Rename
Renames one or more files. Use the ren or rename commands to rename a file.
Syntax: REN [drive:][path]filename1 filename2
Example: Below
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 file1.txt
C:\temp>ren file1.txt newfile.txt
C:\temp>dir
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> .
01/09/2024 02:53 AM <DIR> ..
01/09/2024 02:53 AM 1 newfile.txt
Navigating through the file system efficiently is the cornerstone of Windows administration.
How do I run Windows CMD Shell or Power Shell in Admin mode?
You can run the Windows Command Prompt or Windows Power Shell in Admin mode in two ways.
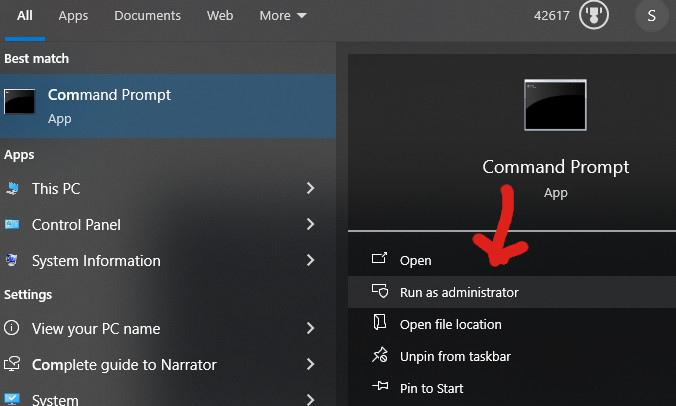
1. Run from Start menu
Go to the start menu and search for Command. Once the CMD Prompt icon appears click on the right side option “Run as Administrator“.
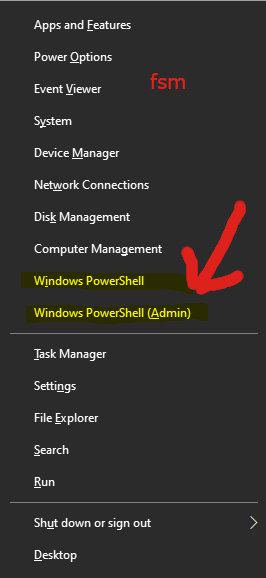
2. Run from Windows context menu options.
From anywhere in Windows type Ctrx + X. In the context menu that appears, select the CMD Shell with the (Admin) option.
User and Group Management Commands
User and group management is crucial for maintaining a secure and organized system. Understand how to create, modify and delete user accounts and groups using command line prompts.
I will be using the net command to show how to manage users and groups.
net user: Manage user accounts
Syntax:
net user [username [password | *] [options]] [/DOMAIN]
username {password | *} /ADD [options] [/DOMAIN]
username [/DELETE] [/DOMAIN]
username [/TIMES:{times | ALL}]
username [/ACTIVE: {YES | NO}]
Example 1: Show existing users
C:\temp>net user
User accounts for \\DESKTOP-B93B7QQ
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator DefaultAccount Guest
guru WDAGUtilityAccount
The command completed successfully.Entering just the net user command show all the current users in the system.
Example 2: Add a new user
In the example below I am creating a user nothing with the password test.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> net user nothing test /add
The command completed successfully.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> net user
User accounts for \\DESKTOP-B93B7QQ
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator DefaultAccount Guest
nothing sohail WDAGUtilityAccount
The command completed successfully.Note: You need to run the add user command from an Admin command shell. Use Ctrl + X keys to bring up a context menu and then select the admin CMD shell.
Example 3: Delete existing user
In the example below I will delete a user with the name nothing, I created in Example 2 above.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> net user nothing /delete
The command completed successfully.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> net user
User accounts for \\DESKTOP-B93B7QQ
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator DefaultAccount Guest
sohail WDAGUtilityAccount
The command completed successfully.net group: Manage user groups
Use the net group command to manage groups on a Windows domain controller. Note, that you cannot run this command on a PC that is not added to a domain controller.
Syntax:
[groupname [/COMMENT:”text”]] [/DOMAIN]
groupname {/ADD [/COMMENT:”text”] | /DELETE} [/DOMAIN]
groupname username […] {/ADD | /DELETE} [/DOMAIN]
Example 1: List Groups
C:\> net groupExample 2: Add Group
net myowngroup /ADD /MYDOMAINExample 3: Delete Group
C:\> net group myowngroup /DELETE / MYDOMAINExample 4: Add User to a Group
C:\> net group myowngroup guru /ADD /MYDOMAINwhoami: Display current logged in user information
whoami utility can be used to get user name and group information along with the respective security identifiers (SID), claims,
privileges, logon identifier (logon ID) for the current user on the local system
WhoAmI has three ways of working:
Syntax 1:WHOAMI [/UPN | /FQDN | /LOGONID]
Syntax 2:WHOAMI { [/USER] [/GROUPS] [/CLAIMS] [/PRIV] } [/FO format] [/NH]
Syntax 3:WHOAMI /ALL [/FO format] [/NH]
Example 1: Get your username
C:\temp>whoami
desktop-b93b7qq\guruExample 2: Get username and SID
C:\temp>WHOAMI /USER
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
====================== ==============================================
desktop-b93b7qq\guru S-1-5-21-1331082015-4267983169-2776141181-1001Example 3: Get all of my user information
C:\temp>whoami/all
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
====================== ==============================================
desktop-b93b7qq\guru S-1-5-21-1331082015-4267983169-2776141181-1001
GROUP INFORMATION
-----------------
Group Name Type SID Attributes
============================================================= ================ ============ ==================================================
Everyone Well-known group S-1-1-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Local account and member of Administrators group Well-known group S-1-5-114 Group used for deny only
BUILTIN\Administrators Alias S-1-5-32-544 Group used for deny only
BUILTIN\Users Alias S-1-5-32-545 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE Well-known group S-1-5-4 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
CONSOLE LOGON Well-known group S-1-2-1 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users Well-known group S-1-5-11 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\This Organization Well-known group S-1-5-15 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Local account Well-known group S-1-5-113 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
LOCAL Well-known group S-1-2-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\NTLM Authentication Well-known group S-1-5-64-10 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-8192
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ==================================== ========
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone DisabledNetwork Configuration
Network issues can be resolved swiftly using command line prompts. You can use these commands to diagnose and troubleshoot network problems effectively.
getmac : Get MAC Address
getmac command enables an administrator to display the MAC address for network adapters on a system.
Syntax:
Example 1: Get MAC address of all adapters on a system.
C:\temp>getmac
Physical Address Transport Name
=================== ==========================================================
E0-4F-43-70-05-90 Media disconnected
10-7B-44-90-30-66 Media disconnected
10-7B-44-8F-A2-D4 \Device\Tcpip_{DEEFE6A0-4ACB-4589-9748-94CB92DE03A3}
E0-4F-43-70-05-91 Media disconnected
00-FF-08-E8-9F-F3 \Device\Tcpip_{08E89FF3-496D-4E32-8CFE-C7BCC74248FF}
00-50-56-C0-00-01 \Device\Tcpip_{61563FF8-5DBB-46D1-B3AD-14D38D145F74}
00-50-56-C0-00-08 \Device\Tcpip_{05773400-658E-4442-BF06-CB6F18FE5463}Note: I find the ipconfig command is more user friendly as it provides the IP address along with the MAC address. But when using scripts to extract MAC information then getmac is a better option.
ipconfig : Display network configuration
ipconfig command is to manage network adapter info and connectivity in a Windows PC and Server.
Syntax: ipconfig [/allcompartments] [/? | /all | /renew [adapter] | /release [adapter] | /renew6 [adapter] | /release6 [adapter] | /flushdns | /displaydns | /registerdns | /showclassid adapter | /setclassid adapter [classid] | /showclassid6 adapter | /setclassid6 adapter [classid] ]
Example 1: List all network Adapter details
C:\temp>ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Unknown adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::82f7:b3b1:a29c:173d%4
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 10.2.18.78
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
Ethernet adapter Ethernet:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Ethernet adapter Ethernet 2:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::b8ca:c6bf:3994:6bec%20
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.100.184
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.100.1
Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Wireless LAN adapter Local Area Connection* 1:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Ethernet adapter Bluetooth Network Connection:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :netstat : View Current TCP/IP Network Connections
Using netstat you can get information on all current network ports being used for communications over the networks.
Syntax: NETSTAT [-a] [-b] [-e] [-f] [-n] [-o] [-p proto] [-r] [-s] [-t] [-x] [-y] [interval]
Command options:
- a : display all connections
- b : Display the executable using the specific connection
- f : Display FQDN (fully qualified domain name) for a connection
- interval : Update interval in seconds
Example: Get port information with the executable
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> netstat -a -b
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
RpcSs
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
Can not obtain ownership information
TCP 0.0.0.0:1844 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
[ElgatoAudioControlServer.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:5040 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
CDPSvc
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:7680 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
Can not obtain ownership information
TCP 0.0.0.0:28198 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
[StreamDeck.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49664 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
[lsass.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49665 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
Can not obtain ownership information
TCP 0.0.0.0:49666 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
EventLog
[svchost.exe]
TCP 0.0.0.0:49668 DESKTOP-B93B7QQ:0 LISTENING
[spoolsv.exe]
TCP 10.2.18.78:54259 wn-in-f188:5228 ESTABLISHED
[chrome.exe]NSLookup : Name Server Lookup
nslookup is an easy to use command to query name server information. You can use it to quickly get information for a single host or elect to use it in interactive mode for multiple queries.
Syntax:
- nslookup [-opt …] # interactive mode using default server
- nslookup [-opt …] – server # interactive mode using ‘server’
- nslookup [-opt …] host # just look up ‘host’ using default server
- nslookup [-opt …] host server # just look up ‘host’ using ‘server’
Example 1: Use nslookup to get ip address of google.com
C:\temp>nslookup google.com
Server: UnKnown
Address: 10.0.0.243
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: google.com
Addresses: 2a00:1450:4019:80e::200e
172.217.19.206Example 2: Use nslookup in interactive mode
C:\Users\sohail>nslookup
Default Server: UnKnown
Address: 10.0.0.243
> google.com
Server: UnKnown
Address: 10.0.0.243
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: google.com
Addresses: 2a00:1450:4019:80e::200e
172.217.19.206
> yahoo.com
Server: UnKnown
Address: 10.0.0.243
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: yahoo.com
Addresses: 2001:4998:124:1507::f001
2001:4998:124:1507::f000
2001:4998:24:120d::1:1
2001:4998:44:3507::8000
2001:4998:24:120d::1:0
2001:4998:44:3507::8001
98.137.11.164
74.6.143.25
74.6.143.26
74.6.231.20
74.6.231.21
98.137.11.163ping: Check network connectivity
Ping is used to check network connectivity by opening a connection to a host and sending it echo requests.
Syntax: ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL] [-v TOS] [-r count] [-s count] [[-j host-list] | [-k host-list]] [-w timeout] [-R] [-S srcaddr] [-c compartment] [-p] [-4] [-6] target_name
Example: Check if a host is available on the network
C:\temp>ping yahoo.com -n 3
Pinging yahoo.com [74.6.143.25] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 74.6.143.25: bytes=32 time=255ms TTL=49
Reply from 74.6.143.25: bytes=32 time=247ms TTL=49
Reply from 74.6.143.25: bytes=32 time=438ms TTL=49
Ping statistics for 74.6.143.25:
Packets: Sent = 3, Received = 3, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 247ms, Maximum = 438ms, Average = 313mstracert: Trace a route to a destination
tracert is a command available in Windows, to help examine network path that Internet traffic takes from their computer (source system) to a remote system, such as a Google server. tracert provides IP addresses and the total number of hops for a source TCP/IP packet to reach its destination.
Syntax: tracert [-d] [-h maximum_hops] [-j host-list] [-w timeout] [-R] [-S srcaddr] [-4] [-6] target_name
tracert Command Options:
- -h maximum_hops Maximum number of hops to search for target.
- -j host-list Loose source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
- -w timeout Wait timeout milliseconds for each reply.
- -R Trace round-trip path (IPv6-only).
- -S srcaddr Source address to use (IPv6-only).
- -4 Force using IPv4.
- -6 Force using IPv6.
Example : Get route to google.com
C:\temp>tracert google.com
Tracing route to google.com [172.217.19.206]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 46 ms 47 ms 46 ms 10.2.18.1
2 * * 2670 ms 95.181.234.1
3 49 ms 55 ms 59 ms ae101-3101.bb1.dxb1.ae.m247.ro [83.97.21.128]
4 51 ms 53 ms 48 ms 185.78.163.233
5 70 ms 63 ms 61 ms ipv6.smarthub-2.uae-ix.as15169.google.com [185.1.8.117]
6 66 ms 64 ms 61 ms 108.170.247.17
7 52 ms 58 ms 55 ms 108.170.238.19
8 59 ms 62 ms 68 ms ams16s31-in-f14.1e100.net [172.217.19.206]
Trace complete.The above path shows there are 8 hops to reach the destination host serving google.com domain. IP address of each hop is show along with the time taken to reach it.
System Information
Keeping track of system resources and processes is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Explore these commands to gain insights into system health.
chkdsk : Check disk files
Checks all files on a disk for integrity and loss prevention and recovery.
Syntax: CHKDSK [volume[[path]filename]]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:size]] [/B] [/scan] [/spotfix]
Example 1: Run chkdsk on C drive for a complete scan.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>chkdsk C:
The type of the file system is NTFS.
WARNING! /F parameter not specified.
Running CHKDSK in read-only mode.
Stage 1: Examining basic file system structure ...
Progress: 1789953 of 1808128 done; Stage: 98%; Total: 34%; ETA: 0:00:15 ..Note: I stopped the scan mid-execution. So the report above is incomplete.
schtasks : Schedule Task
Enables an administrator to create, delete, query, change, run and end scheduled tasks on a local or remote system.
Syntax: SCHTASKS /parameter [arguments]
Parameters to schtasks
- create: Creates a new scheduled task.
- delete: Deletes the scheduled task(s).
- query: Displays all scheduled tasks.
- change: Changes the properties of scheduled task.
- run: Runs the scheduled task on demand.
- end: Stops the currently running scheduled task.
Example 1: Create a new scheduled task
I am going to create a new task named wakemeup to run myapp.exe starting at 12:00 and automatically terminating at 14:00 hours every day
C:\temp>SCHTASKS /Create /SC DAILY /TN wakemeup /TR c:\myapp /ST 12:00
SUCCESS: The scheduled task "wakemeup" has successfully been created.Example 3: List tasks
C:\temp>schtasks /queryExample 2: Delete existing task
I am going to delete the wakemeup task I created earlier in this example.
C:\temp>schtasks /delete /tn wakemeup
WARNING: Are you sure you want to remove the task "wakemeup" (Y/N)? Y
SUCCESS: The scheduled task "wakemeup" was successfully deleted.powercfg: Get power configuration
Enables users to control power settings on a local system. The command gives a report of power settings.
Syntax: POWERCFG /COMMAND [ARGUMENTS]
Example 1: List all power configurations for a system.
C:\temp>powercfg /L
Existing Power Schemes (* Active)
-----------------------------------
Power Scheme GUID: 381b4222-f694-41f0-9685-ff5bb260df2e (Balanced) *
Power Scheme GUID: 8c5e7fda-e8bf-4a96-9a85-a6e23a8c635c (High performance)
Power Scheme GUID: a1841308-3541-4fab-bc81-f71556f20b4a (Power saver)Example 2: List power throttling application settings.
Use the example below to view power usage settings by App.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>powercfg /powerthrottling /list
Battery Usage Settings By App
=============================Note: In my case I don’t have any Apps being throttled. The output will be different per individual system.
schtasks: Schedule Tasks
Enables an administrator to create, delete, query, change, run and end scheduled tasks on a local or remote system.
sfc : System File Checker
Scans the integrity of all protected system files and replaces incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions. This command helps to detect any malware or virus threat by scanning the core system files and identify changes and replace those files.
Note: You need to run this command as an Administrator.
Syntax: SFC [/SCANNOW] [/VERIFYONLY] [/SCANFILE=] [/VERIFYFILE=][/OFFWINDIR= /OFFBOOTDIR= [/OFFLOGFILE=]]
- SCANNOW: Scans integrity of all protected system files and repairs files with problems when possible
- VERIFYONLY: Scans integrity of all protected system files. No repair operation is performed.
- SCNFILE: Scans integrity of the referenced file, repairs file if problems are identified. Specify full path
Example 1: Start a sfc scan with verifyfile option to check if a specific file is corrupt.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>sfc /VERIFYFILE=c:\windows\system32\kernel32.dll
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.shutdown: Turn off Computer
Use this command to shutdown a computer from command line. Like all other commands this can be part of a batch process.
Syntax: shutdown [/i | /l | /s | /sg | /r | /g | /a | /p | /h | /e | /o] [/hybrid] [/soft] [/fw] [/f] [/m \computer][/t xxx][/d [p|u:]xx:yy [/c "comment"]]
The shutdown command has many options and provides the ability to put the computer on sleep, hibernate or shutdown.
The /i option, when used shows a dialog box where you can log your comments about the particular shutdown action.
Example 1: Use pop up dialog to log shutdown reason
C:\temp>shutdown /iEntering the command above show the following dialog.
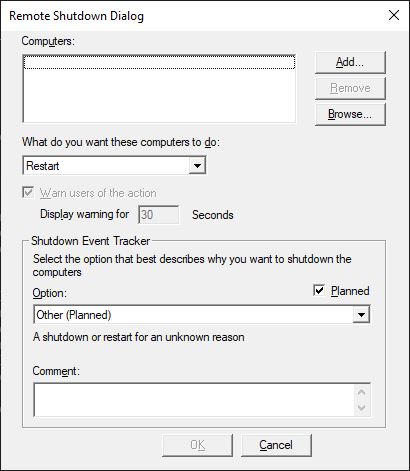
Example 2: Shutdown system from command line in 30 seconds
C:\temp>shutdown /t 30 /fNote: The /f option forces running applications to close without forewarning users.
systeminfo: Display detailed system information
You can use the systeminfo command to view local or remote machines. You can get most if not all configuration information including service pack levels.
Syntax: SYSTEMINFO [/S system [/U username [/P [password]]]] [/FO format] [/NH]
Example 1: Get all system information
C:\temp>systeminfo
Host Name: DESKTOP-B93B7QQ
OS Name: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
OS Version: 10.0.19045 N/A Build 19045
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Standalone Workstation
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: sohail
Registered Organization: N/A
Product ID: 04750-50300-06660-ET436
Original Install Date: 10/12/2023, 11:20:39 AM
System Boot Time: 1/9/2024, 1:48:31 AM
System Manufacturer: System manufacturer
System Model: System Product Name
System Type: x64-based PC
Processor(s): 1 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: AMD64 Family 23 Model 1 Stepping 1 AuthenticAMD ~3500 Mhz
BIOS Version: American Megatrends Inc. 0902, 12/21/2017
Windows Directory: C:\WINDOWS
System Directory: C:\WINDOWS\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Input Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Time Zone: (UTC-08:00) Pacific Time (US & Canada)
Total Physical Memory: 32,641 MB
Available Physical Memory: 16,832 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 37,505 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 11,486 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 26,019 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: WORKGROUP
Logon Server: \\DESKTOP-B93B7QQ
Hotfix(s): 12 Hotfix(s) Installed.
[01]: KB5032005
[02]: KB5030841
[03]: KB5003791
[04]: KB5011048
[05]: KB5015684
[06]: KB5020683
[07]: KB5026037
[08]: KB5033372
[09]: KB5031539
[10]: KB5032392
[11]: KB5032907
[12]: KB5005699
Network Card(s): 7 NIC(s) Installed.
[01]: Qualcomm Atheros QCA61x4A Wireless Network Adapter
Connection Name: Wi-Fi
Status: Media disconnected
[03]: ROG AREION 10G
Connection Name: Ethernet 2
DHCP Enabled: Yes
DHCP Server: 192.168.100.1
IP address(es)
[01]: 192.168.100.184
[02]: fe80::b8ca:c6bf:3994:6bec
[04]: Bluetooth Device (Personal Area Network)
Connection Name: Bluetooth Network Connection
Status: Media disconnected
[05]: Private Internet Access Network Adapter
Connection Name: Local Area Connection
Status: Media disconnected
Hyper-V Requirements: VM Monitor Mode Extensions: Yes
Virtualization Enabled In Firmware: Yes
Second Level Address Translation: Yes
Data Execution Prevention Available: Yes- tasklist and taskkill: List and kill current running processes
Event Viewer Commands
Analyzing and monitoring events are essential for identifying and resolving issues. Discover how to efficiently use these commands to extract valuable information from the event log.
wevtutil : Query and Manage Event Logs
Windows Events Command Line Utility.
wevtutil enables you to retrieve information about event logs and publishers, install and uninstall event manifests, run queries, and export, archive, and clear logs.
Syntax: wevtutil COMMAND [ARGUMENT [ARGUMENT] …] [/OPTION:VALUE [/OPTION:VALUE] …]
- Clear-Eventlog: Clear specified event logs
- get-eventlog: Retrive events from classic event logs
- wevtutil: Query and manage event logs
Command options
- el : List log names
- gl : Get log configuration information
- sl : Modify configuration of a log
- ep : List event publishers
- qe : Query events from a log or log files
Example 1: Get list of all event logs
C:\temp>wevtutil el
AMSI/Debug
AirSpaceChannel
Analytic
Application
DirectShowFilterGraph
DirectShowPluginControl
Els_Hyphenation/Analytic
EndpointMapper
FirstUXPerf-Analytic
ForwardedEvents
General Logging
HardwareEvents
...
--- truncated for brevityExample 2: Get details for a specific log by name
C:\temp>wevtutil gl Application
name: Application
enabled: true
type: Admin
owningPublisher:
isolation: Application
channelAccess: O:BAG:SYD:(A;;0x2;;;S-1-15-2-1)(A;;0x2;;;S-1-15-3-1024-3153509613-960666767-3724611135-2725662640-12138253-543910227-1950414635-4190290187)(A;;0xf0007;;;SY)(A;;0x7;;;BA)(A;;0x7;;;SO)(A;;0x3;;;IU)(A;;0x3;;;SU)(A;;0x3;;;S-1-5-3)(A;;0x3;;;S-1-5-33)(A;;0x1;;;S-1-5-32-573)
logging:
logFileName: %SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\Application.evtx
retention: false
autoBackup: false
maxSize: 20971520
publishing:
fileMax: 1Other Useful Windows Command Line Prompts
bitsadmin: Transfer Files
bitsadmin is a versatile command on Windows, which I use to download files from the internet. For me it is a great alternative to the Linux command wget.
Syntax: USAGE: BITSADMIN [/RAWRETURN] [/WRAP | /NOWRAP] command
Commands available with bitsadmin
- LIST: List all jobs
- RESET: Deletes all jobs in the queue
- TRANSFER: Upload or download , one or more files.
There are many more commands available to use with bitsadmin. Use /? to view all available options.
Example 1: Download file from internet with bitsadmin
C:\temp>bitsadmin /transfer getwp /download /priority normal https://wordpress.org/latest.zip C:\temp\wp.zip
DISPLAY: 'getwp' TYPE: DOWNLOAD STATE: TRANSFERRING
PRIORITY: NORMAL FILES: 0 / 1 BYTES: 1899 / 25954973 (0%)
TRANSFER RATE: 95.31 B/S TIME REMAINING: 3 daysNote: For more examples of bitsadmin, check out Microsoft website.